Testing
Test each part of your code to verify that you’ve implemented it correctly.
You should try and test as many scenarios as possible to make sure a purchase won't be left in an invalid state.
The following is a list of some common ones that you should test.
Test a Payment Request
Make a call to makePurchase using a valid product identifier that you have already tested.
Set a breakpoint and confirm that the purchase success event handler is called.
During testing, it’s OK to finish the transaction immediately without providing the content. However, even during testing, failing to finish the purchase can cause problems, unfinished purchases can remain in the queue indefinitely, which could interfere with later testing.
Test a Successful Purchase
Use a test user account, and make a purchase in your app.
Set a breakpoint at the point in your code that adds the purchase to your users inventory, and confirm that this code is called in response to a successful purchase.
Cancellation
Check that when a user cancels the purchase that your application correctly handles the response and returns your application to the normal state.
You will need to handle several scenarios here, including a cancelled purchase and a cancelled error.
See Handling User Cancellations for implementation details.
Testing Deferred Purchases
Google Play Billing
You will need to target api 28 or higher for deferred purchases.
When you go to make a purchase ensure you have deployed at least one version to the a test channel (alpha/beta) and are signed in on your device using a test user.
Then when the purchase UI is displayed select the payment methods and you should see 4 available options:
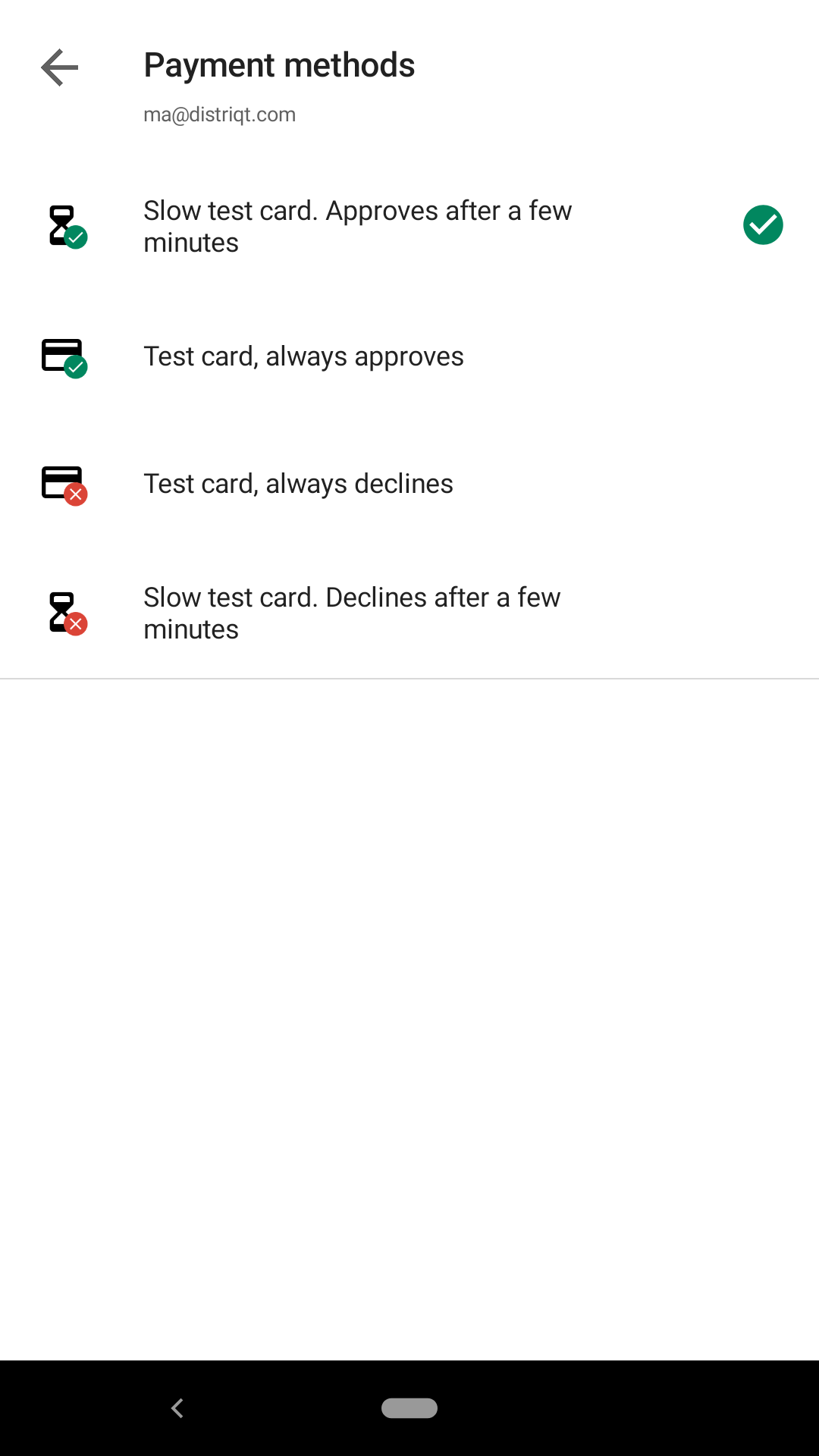
Select the "Slow test card" and proceed with your test purchase:
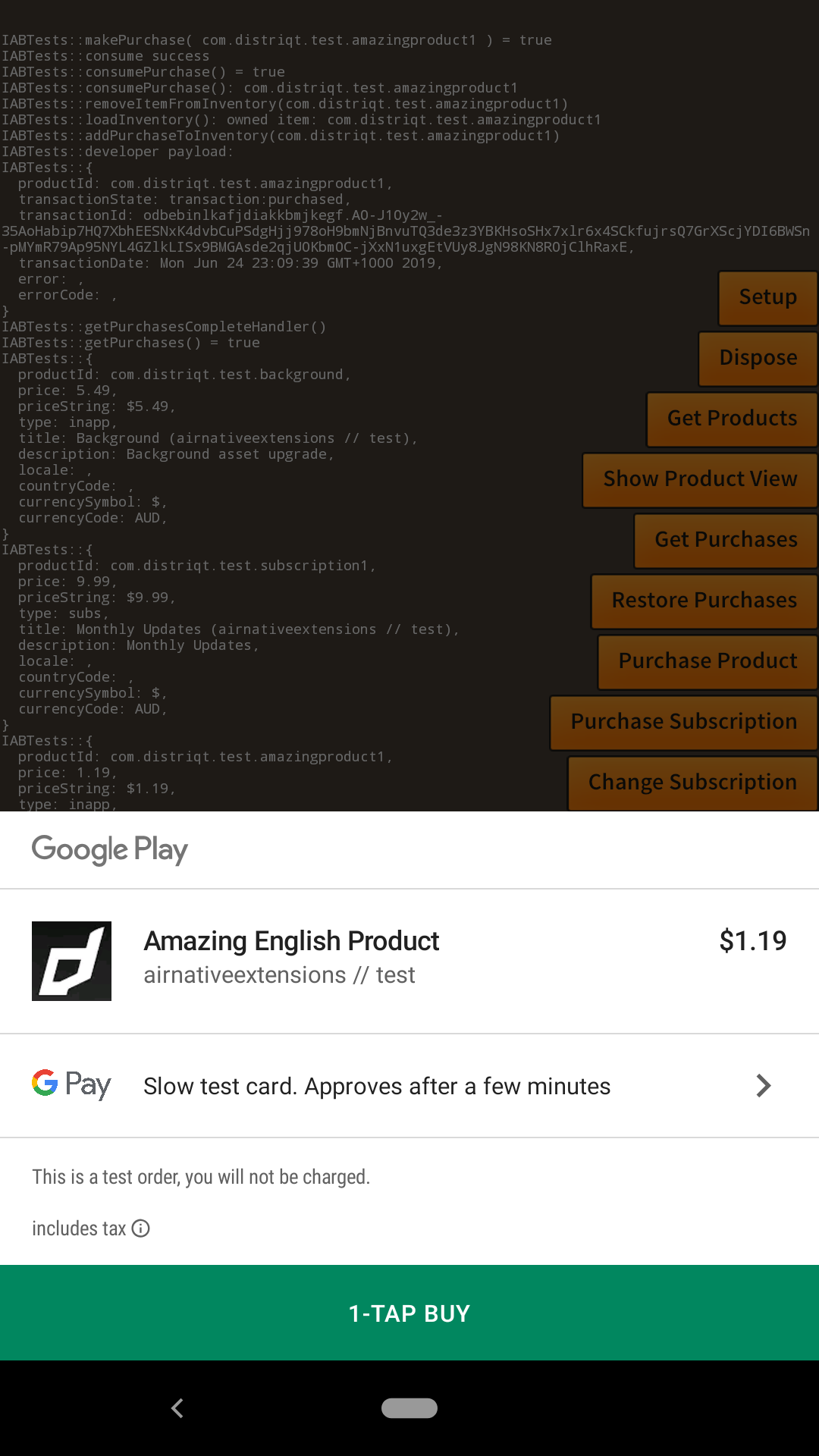
The purchase will return as deferred and in a few minutes another event will trigger when the purchase succeeds. On the second event you should deliver the product and call finish purchase to acknowledge the purchase.
Test an Interrupted Purchase
On some services, purchases can be interrupted, it is important, particularly on iOS that you can handle interrupted transactions.
Set a breakpoint in your code that adds the purchase to your users inventory so you can control whether it delivers the product.
Then make a purchase as usual in the test environment, and use the breakpoint to
temporarily ignore the transaction—for example, by returning from the method immediately.
Do not call finishPurchase.
Terminate and relaunch your app.
The extension should dispatch the PURCHASES_UPDATED event when you call setup the service
again shortly after launch; this time, let your app respond normally.
Verify that your app correctly delivers the product and completes the transaction.
This is only applicable for services that require calling
finishPurchase, mainly the Apple's In-App Purchases.
Verify That Purchases Are Finished
Locate where your app calls the finishPurchase method. You should call this whether or not
the service you are using requires it.
Verify that all work related to the transaction has been completed before the method is called and that the method is called for every transaction, whether it succeeded or failed.