Requesting Access
When you are going to be accessing a 'dangerous' permission you must check that your application has been allowed access.
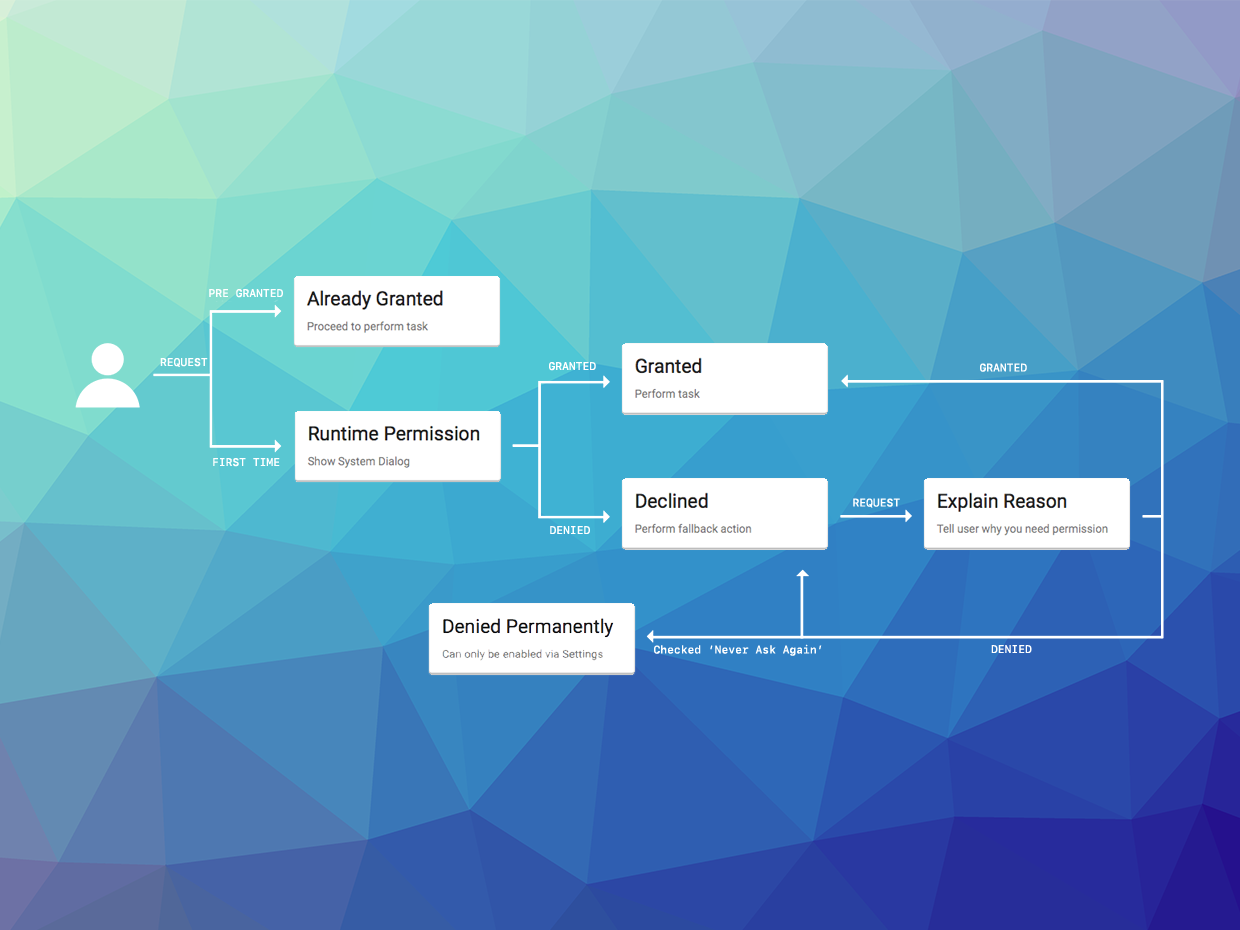
On Android these permissions are listed through the manifest additions. On older versions of Android these permissions are accepted when the user installs the application. More modern versions (Marshmallow 6 [API v23]+) require that you request the permissions similar to iOS. You will still need to list them in your manifest and then follow the same code below.
Individual Permissions
Instead of using multiple permissions together it is often more important to request permissions individually and when appropriate functionality is being used in your application (eg requesting camera permission when the user requests to take a photo).
Check Authorisation Status
You can check the authorisation status for a specific permission by using the authorisationStatusForPermission() method:
- AIR
- Unity
var status:String = Permissions.instance.authorisationStatusForPermission( "android.permission.CAMERA" );
string status = Permissions.Instance.AuthorisationStatusForPermission("android.permission.CAMERA");
status can be one of the values defined in the AuthorisationStatus class:
AuthorisationStatus.AUTHORISED: This device has been authorised.AuthorisationStatus.NOT_DETERMINED: You are yet to ask for authorisation.AuthorisationStatus.SHOULD_EXPLAIN: You need to further explain.AuthorisationStatus.DENIED: The user has disabled the permission.AuthorisationStatus.UNKNOWN: The permission is in an unknown state, normally indicating an error has occurred.AuthorisationStatus.RESTRICTED: The user has restricted the permission to certain assets.
Request Authorisation
To request authorisation for an individual permission you can use the requestAuthorisationForPermission() method passing the permission of interest.
- AIR
- Unity
Permissions.instance.requestAuthorisationForPermission( "android.permission.CAMERA" );
Permissions.Instance.RequestAuthorisationForPermission( "android.permission.CAMERA" );
This method can either be handled with an event result or via a callback function.
Event
You will receive an AuthorisationEvent.CHANGED (or AuthorisationEvent.PERMISSION_CHANGED) event after the process completes which contains the updated status:
- AIR
- Unity
Permissions.service.addEventListener( AuthorisationEvent.CHANGED, authorisationChangedHandler );
Permissions.service.requestAuthorisationForPermission( "android.permission.CAMERA" );
You will then receive a change event if the user accepted your permission request:
function authorisationChangedHandler( event:AuthorisationEvent ):void
{
// Check the authorisation state again (as above)
}
Permissions.Instance.OnAuthorisationChanged += Permissions_OnAuthorisationChanged;
Permissions.service.RequestAuthorisationForPermission( "android.permission.CAMERA" );
You will then receive a change event if the user accepted your permission request:
private void Permissions_OnAuthorisationChanged(AuthorisationEvent e)
{
// Check the authorisation state again (as above)
}
Callback
You can supply a function to the requestAuthorisationForPermission() method that will be called when the process completes.
This method should have the following signature function( status:String ):void.
The status parameter is the updated authorisation status.
- AIR
- Unity
Permissions.instance.requestAuthorisationForPermission(
"android.permission.CAMERA",
function ( status:String ):void
{
trace( "requestAuthorisationForPermission(): status=" + status );
// Check the authorisation state again (as above)
} );
Permissions.Instance.RequestAuthorisationForPermission(
"android.permission.CAMERA",
(string status) =>
{
Log("request auth status = " + status);
// Check the authorisation state again (as above)
}
);
Multiple Permissions
You can use the extension to handle multiple permissions by passing an array of permissions to the extension and then using the following functionality to check for authorisation status of all the permissions combined.
Set Permissions
You must inform the extension which permissions you wish to request.
This is done by passing an array of Strings each being the permission required.
For example to set the camera permission:
- AIR
- Unity
Permissions.service.setPermissions(
[
"android.permission.CAMERA"
]
);
Permissions.Instance.SetPermissions(
[
"android.permission.CAMERA"
]
);
Check Authorisation
You can check the current authorisation status by calling the authorisationStatus() method:
- AIR
- Unity
switch (Permissions.service.authorisationStatus())
{
case AuthorisationStatus.AUTHORISED:
// This device has been authorised.
break;
case AuthorisationStatus.NOT_DETERMINED:
case AuthorisationStatus.SHOULD_EXPLAIN:
// You are yet to ask for authorisation or need to further explain
// At this point you should consider your strategy to get your
// user to authorise by explaining your need for the permissions
break;
case AuthorisationStatus.DENIED:
case AuthorisationStatus.UNKNOWN:
case AuthorisationStatus.RESTRICTED:
// The user has disabled the permissions
// Advise your user of the lack of permissions as you see fit
break;
}
TODO
You should respect the SHOULD_EXPLAIN status by displaying additional information
to your user about why you require this functionality.
Request Authorisation
To request authorisation call the requestAuthorisation() function.
You can either wait for the event or supply a callback function to get details on when the request authorisation process completes.
Event
You will receive an AuthorisationEvent.CHANGED event after the process completes which contains the updated status:
- AIR
- Unity
Permissions.service.addEventListener( AuthorisationEvent.CHANGED, authorisationChangedHandler );
Permissions.service.requestAuthorisation();
You will then receive a change event if the user accepted your permission request:
function authorisationChangedHandler( event:AuthorisationEvent ):void
{
// Check the authorisation state again (as above)
}
Permissions.Instance.OnAuthorisationChanged += Permissions_OnAuthorisationChanged;
Permissions.service.RequestAuthorisation();
You will then receive a change event if the user accepted your permission request:
private void Permissions_OnAuthorisationChanged(AuthorisationEvent e)
{
Debug.Log("Permissions_OnAuthorisationChanged");
}
Callback
You can supply a function to the requestAuthorisation() method that will be called when the process completes. This method should have the following signature function( status:String ):void. The status parameter is the updated authorisation status.
- AIR
- Unity
Permissions.instance.requestAuthorisation(
function ( status:String ):void
{
trace( "requestAuthorisation(): status=" + status );
// Check the authorisation state again (as above)
} );
Permissions.Instance.RequestAuthorisation(
(string status) =>
{
Log("request auth status = " + status);
}
);
Example
- AIR
- Unity
function checkAndRequestAuthorisation():void
{
switch (Permissions.service.authorisationStatus())
{
case AuthorisationStatus.AUTHORISED:
// This device has been authorised.
break;
case AuthorisationStatus.NOT_DETERMINED:
// You are yet to ask for authorisation
Permissions.service.addEventListener( AuthorisationEvent.CHANGED, authorisationChangedHandler );
Permissions.service.requestAuthorisation();
break;
case AuthorisationStatus.SHOULD_EXPLAIN:
// At this point you should consider your strategy to get your
// user to authorise by explaining your need for the permissions
// You can attempt a request again or show a dialog as to the requirement for the permission
break;
case AuthorisationStatus.DENIED:
case AuthorisationStatus.UNKNOWN:
case AuthorisationStatus.RESTRICTED:
// The user has disabled the permissions
// Advise your user of the lack of permissions as you see fit
break;
}
}
function authorisationChangedHandler( event:AuthorisationEvent ):void
{
// Check the authorisation state again (as above)
checkAndRequestAuthorisation();
}
Events
- AIR
- Unity
There are two main events of interest dispatched by this extension.
AuthorisationEvent.CHANGED: Dispatched when the authorisation status has changed. This is independent of any particular permission and just indicates something has changed.AuthorisationEvent.PERMISSION_CHANGED: Dispatched when the authorisation status of a specific permission changes. The event contains the permission and the new status. If you are using the "multiple permissions" approach you may receive multiple of these events after a request authorisation process has completed.
.